Message Trace in Office / Microsoft 365
- ALIF Consulting
- Mar 10, 2022
- 7 min read
Updated: Dec 9, 2024
What is Message Trace
Message Trace is the mechanism to determine whether an electronic message [E-mail] travelling over the internet is being sent/received by a sender and a recipient.
Unlike Microsoft Exchange as an Email Service Provider, there are multiple other providers, such as Google, Yahoo, Domino, etc, who do the same process, but we would be focusing on Microsoft Exchange Services, which is further divided into on-premises and online, which is the Cloud Mail Services.
Message trace follows email messages as they travel through your Exchange Online organization. You can determine if a message was received, rejected, deferred, or delivered by the service. It also shows what actions were taken on the message before it reached its final status.
Why Message Trace
Message trace is the tool/utility / or a modulated program which allows us to confirm whether an email sent by a sender is received or not.
Similarly, the recipient side admin can also confirm if the email sent by the sender entered into his organization or not and where the email was delivered. This tool allows the administrator to confirm what specific action was taken on the email.
Message Trace follows email messages as they travel through Exchange Online Protection. You can determine if an email message was received, rejected, deferred, or delivered by the service. It also shows what actions were taken on the message before it reached its final status.
Types of Message Trace
In Office 365, you can perform message traces either through GUI or through PowerShell commands.
Ideally, there are two types of message trace through which one can get the results and confirm what usually happens with the message.
Normal Message Trace: This is a real-time message trace that usually gives instant results.
We can perform this trace usually for the past 7 days through the Classic Exchange Admin Center and 10 days from the New Admin Center or the Microsoft Defender Portal.
Extended Message Trace: As the name suggests, extended this gives a detailed flow of the message and generates the result in approx. 2 hours for a message event.
You can pull a message trace report with this trace type for the past 90 days, but you need to be sure that the message trace result is going to take some time and will not be instant. Even if we need to perform a detailed message trace within the past 7 days, we need to give the date for more than 7 days so that it creates an in-detailed report.
Who can Perform a Message Trace?

Like any action in Office 365, message trace search requires certain permissions or roles
Security Admin
Security Reader
View-Only Recipients
Compliance Admin
Data Loss Prevention
By default, role group Organization Management has all of the required permissions.
You need to be a Global Administrator or an Exchange Administrator, which indeed has all these above-mentioned roles, so they get access to the Message Trace portal and can perform the message trace.
Message tracing does not allow you to peek into a message’s contents. Still, it can provide quite a lot of important data about emails:
Sender and Recipient
Send and receive dates
Subject and size
Status and details of events. There are seven possible values in the delivery status field: delivered, failed, pending, expanded, quarantined, filtered as spam, and unknown.
IP address used to send the message
Message ID is a unique number identifying a message. If a message is sent to more than one recipient, it will display once for every recipient in the message trace search, but all those entries will have the same Message ID and different Message Trace ID
Practical application of message tracking
Message tracing makes it possible to learn what happened to certain messages, even if they are not delivered or get deleted. There are quite a few different uses for this kind of information:
Find and fix mail-delivery issues – the most basic and ‘traditional’ purpose for message tracing. Whenever a user or a client reports that some message seems to be missing, administrators can get to the bottom of the problem. Of course, finding the right message quickly depends on how much info the user provides. Finding a message that “someone was supposed to send me last week” might take a while, especially in larger organizations
Monitor mail flow – as message tracing collects data about all messages processed within the organization, the results can be used to gather statistical data.
Check if your mail flow rules work the way they should – it is not hard to make a mistake while configuring mail flow rules, especially in a large organization and when there are possible conflicts between different rules. As message tracing details provide detailed information about failures, you will be able to pinpoint which mail flow rule is at fault.
Message forensics – although message tracking logs and results of message tracing do not let the Administrator into the contents of an email, information about the sender, recipients, date, time, and size of the message can prove very valuable, for example, in case of litigation. If an important email is purged before a litigation hold or a retention policy is activated, logs can act as key evidence.
Want to learn how message trace works in Office 365? Check out our exciting video with a live demo and easy-to-follow explanation!
Office 365 message tracing using PowerShell
You can use PowerShell to search through message tracking logs on on-premises servers as well as to trace messages in Exchange Online.
Get-Message Trace
Get-Message Trace does not require any additional parameters; however, if you do not add any, it will return information about all messages processed by your tenant in the last 48 hours. Normally, that would provide you with too much data for diagnostic purposes. To find out what happened to a specific email, you will need to narrow your query down.
For example:
Get-MessageTrace -RecipientAddress <user’s address> -StartDate 11/07/2017 -EndDate 11/14/2017

This cmdlet shows all mail flow directed to the user between the defined dates. If it does not give all the required details, change the format of the results and specify the properties you need, like FromIP or Size
Get-Message Trace Detail
To check what happened to the message, for example, why did the delivery fail, you will need the Get-Message Trace Detail. Instead of finding and copying the Message Trace ID from the results of the previous cmdlet, let’s just use it in a pipeline:
Get-Message Trace -Recipient Address <user’s address> -Start Date 11/07/2017 -End Date 11/14/2017 -Status Failed | Get-Message Trace Detail

As you can easily see, the delivery failed because of a mail flow rule. This is one of the reasons you should always take a second to name mail flow rules properly. A name like “Rule 1” probably will not tell you much, even if you were the one to set up the rule in the past.
Start-HistoricalSearch
Running a message trace for emails older than a week is not possible directly; it requires running a Historical Search. To begin the search, run Start-HistoricalSearch. The required parameters are StartDate, EndDate, ReportTitle and ReportType (MessageTrace or MessageTraceDetail). Make sure you have also specified the -NotifyAddress field to receive the report as soon as it is ready. If the -NotifyAddress parameter is not specified, the only way to access the report is via EAC. Also, it is important to narrow down the search to include only the data you need, as a historical search might take up to a few hours.
Start-HistoricalSearch -ReportTitle "Trace1" -ReportType MessageTrace -SenderAddress j.stone@mod099.onmicrosoft.com -StartDate 11/01/2017 -EndDate 11/07/2017 -NotifyAddress j.stone@mod099.onmicrosoft.com
To check the status of any search started in the last ten days, use Get-HistoricalSearch.
Message tracking in Office 365 using EAC
On-prem Exchange did not allow message tracking via the Exchange admin centre. In Office 365, EAC enables message tracing and offers quite a comfortable experience. Although usually I prefer administrating Exchange Online with PowerShell, I must say that in this case, EAC seems to do its job very efficiently.
To access Message trace, you can either use this link or go to Exchange admin center > Mail flow > Message trace :

Now, you can either click Start a trace to specify your search criteria from scratch or use one of the templates available below. Templates open the same New message trace window, but they have some fields predefined.

This window lets you define the criteria for the reports you want to generate. You can define the following criteria:
Senders – defines senders the tool will incorporate in the reports. The field accepts wildcards, which allows you to easily limit results for a certain domain.
Recipients – similar to the Senders fields, it accepts wildcards.
Time range – can be configured by using a slider or entering a custom time range.
Additionally, you can click Detailed search options to make your query even more granular:
Delivery status – lets you search only for the emails which were, for example, successfully delivered or quarantined. For a list of all available statuses and what they mean, see this section of the article.
Message ID – lets you find a specific message. Message ID can be found in the email’s headers.
Direction – lets you choose from Inbound, Outbound and All.
Original client IP address.
Remember, tracing messages older than ten days is treated like a Historical Search, no matter if you use EAC or PS. It means that you will have to wait for your reports either way. Generating the reports might take up to a few hours. If you trace messages from the past ten days, clicking search will open a window with the results:

If you want to see details for a chosen email, click it, and a new window will open:
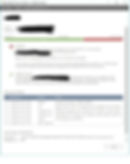
In this window, you can check what happened to the message. In the example above, you can see that the delivery failed because of a transport rule. You can easily check which transport rule caused the problem and fix the issue.
Back in the main message trace window, you can go to the Downloadable Reports tab to see a list of the historical searches and extended reports you have requested. If you have started a Historical Search using PowerShell and failed to specify the –Notify Address parameter, this is the only place to learn if the message trace is finished and to download the csv file with your report.

The downloaded report is in the CSV format. Each row displays information about a single email. To make your report more readable, you can open it in Excel or another spreadsheet.
